/* A
Bison parser, made from pas(2).y
by GNU Bison version 1.25
*/
#define YYBISON 1
/* Identify Bison output. */
#define alloca
#define yyerror error
#define OPREL 258
#define OPSuma 259
#define OPAsigna 260
#define DOSP 261
#define PTOCOMA 262
#define COMA 263
#define PTO 264
#define OPMult 265
#define PABRE 266
#define PCIERRA 267
#define PABREC 268
#define PCIERRAC 269
#define PROG 270
#define VAR 271
#define ARR 272
#define OF 273
#define INT 274
#define REAL 275
#define FUNC 276
#define PROC 277
#define BEG 278
#define END 279
#define IF 280
#define THEN 281
#define ELSE 282
#define WHILE 283
#define DO 284
#define FOR 285
#define TO 286
#define ID 287
#define NUM 288
#define LLAVEA 289
#define LLAVEC 290
#line 2 "pas(2).y"
extern int error(char* msg);
extern int ln;
extern char*
yyTexto();
#include <ctype.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include "pas(2).tab.h"
#ifndef YYSTYPE
#define YYSTYPE int
#endif
#include <stdio.h>
#ifndef __cplusplus
#ifndef __STDC__
#define const
#endif
#endif
#define YYFINAL 117
#define YYFLAG 32768
#define YYNTBASE 36
#define YYTRANSLATE(x) ((unsigned)(x) <= 290
? yytranslate[x] : 59)
static const char yytranslate[] =
{ 0,
2, 2,
2, 2, 2,
2, 2, 2,
2, 2,
2, 2,
2, 2, 2,
2, 2, 2,
2, 2,
2, 2,
2, 2, 2,
2, 2, 2,
2, 2,
2, 2,
2, 2, 2,
2, 2, 2,
2, 2,
2, 2,
2, 2, 2,
2, 2, 2,
2, 2,
2, 2,
2, 2, 2,
2, 2, 2,
2, 2,
2, 2,
2, 2, 2,
2, 2, 2,
2, 2,
2, 2,
2, 2, 2,
2, 2, 2,
2, 2,
2, 2,
2, 2, 2,
2, 2, 2,
2, 2,
2, 2,
2, 2,
2, 2, 2,
2, 2, 2,
2, 2,
2, 2, 2,
2, 2, 2,
2, 2,
2, 2,
2, 2, 2,
2, 2, 2,
2, 2,
2, 2,
2, 2, 2,
2, 2, 2,
2, 2,
2, 2,
2, 2, 2,
2, 2, 2,
2, 2,
2, 2,
2, 2, 2,
2, 2, 2,
2, 2,
2, 2,
2, 2, 2,
2, 2, 2,
2, 2,
2, 2,
2, 2, 2,
2, 2,
2, 2, 2,
2, 2,
2, 2, 2,
2, 2, 2,
2, 2,
2, 2,
2, 2, 2,
2, 2, 2,
2, 2,
2, 2,
2, 2, 2,
2, 2, 2,
2, 2,
2, 2,
2, 2, 2,
2, 2, 2,
2, 2,
2, 2,
2, 2, 2,
2, 2, 2,
2, 2,
2, 2,
2, 2, 2,
2, 2, 2,
2, 2,
2, 2,
2, 2, 2,
2, 2, 2,
2, 2,
2, 2,
2, 2, 2,
2, 2, 2,
2, 2,
2, 2,
2, 2, 2,
1, 2, 3,
4, 5,
6, 7,
8, 9, 10,
11, 12, 13,
14, 15,
16, 17,
18, 19, 20,
21, 22, 23,
24, 25,
26, 27,
28, 29, 30,
31, 32, 33,
34, 35
};
#if YYDEBUG != 0
static const short yyprhs[] =
{ 0,
0, 4,
11, 12, 16,
18, 22, 29,
30, 32,
42, 44,
46, 50, 51,
55, 62, 67,
71, 72,
76, 82,
86, 88, 92,
94, 96, 100,
105, 114,
120, 121,
124, 125, 127,
132, 134, 139,
141, 145,
147, 151,
153, 157, 159,
163, 165, 170,
172
};
static const short yyrhs[] =
{ 37,
38, 9,
0, 15, 32,
11, 39, 12,
7, 0,
0, 40,
43, 48, 0,
32, 0, 39,
8, 32,
0, 40,
16, 39, 6,
41, 7, 0,
0, 42,
0, 17,
13, 33, 9,
9, 33, 14,
18, 42,
0, 19,
0, 20, 0,
43, 44, 7,
0, 0,
45, 40,
48, 0, 21,
32, 46, 6,
42, 7,
0, 22,
32, 46, 7,
0, 11, 47,
12, 0,
0, 39,
6, 41, 0,
47, 7, 39,
6, 41,
0, 23,
49, 24, 0,
50, 0, 49,
7, 50,
0, 53,
0, 48, 0,
52, 5, 55,
0, 28,
55, 29,
50, 0, 30,
32, 5, 55,
31, 55,
29, 50,
0, 25, 55,
26, 50, 51,
0, 0,
27, 50,
0, 0, 32,
0, 32, 13,
55, 14,
0, 32,
0, 32, 11,
54, 12, 0,
55, 0,
54, 8,
55, 0, 56,
0, 56, 3,
56, 0,
57, 0,
56, 4, 57,
0, 58, 0,
57, 10,
58, 0,
32, 0, 32,
11, 54, 12,
0, 33,
0, 11,
55, 12, 0
};
#endif
#if YYDEBUG != 0
static const short yyrline[] = {
0,
47, 49,
50, 52, 54,
55, 57, 58,
60, 61,
63, 64,
66, 67, 69,
71, 72, 74,
75, 77,
78, 80,
82, 83, 85,
86, 87, 88,
89, 90,
91, 93,
94, 97, 98,
100, 101, 103,
104, 106,
107, 109,
110, 112, 113,
115, 116, 117,
118
};
#endif
#if YYDEBUG != 0 || defined (YYERROR_VERBOSE)
static const char * const yytname[]
= { "$","error","$undefined.","OPREL",
"OPSuma","OPAsigna","DOSP","PTOCOMA","COMA","PTO","OPMult","PABRE","PCIERRA",
"PABREC","PCIERRAC","PROG","VAR","ARR","OF","INT","REAL","FUNC","PROC","BEG",
"END","IF","THEN","ELSE","WHILE","DO","FOR","TO","ID","NUM","LLAVEA","LLAVEC",
"PROGRAM","encabezado","codigo","lista_id","declaraciones","tipo","tipo_std",
"declaraciones_subp","declaracion_subp","encab_subp","argumentos","lista_parametros",
"prop_compuesta","lista_prop","prop","else","variable","prop_procedimiento",
"lista_expr","expresion","expr_simple","termino","factor",
NULL
};
#endif
static const short yyr1[] = { 0,
36, 37,
37, 38, 39,
39, 40, 40,
41, 41,
42, 42,
43, 43, 44,
45, 45, 46, 46,
47,
47, 48,
49, 49, 50,
50, 50, 50,
50, 50,
50, 51,
51, 52, 52,
53, 53, 54,
54, 55,
55, 56,
56, 57, 57,
58, 58, 58,
58
};
static const short yyr2[] = { 0,
3, 6,
0, 3, 1,
3, 6, 0,
1, 9,
1, 1,
3, 0, 3,
6, 4, 3,
0, 3,
5, 3,
1, 3, 1,
1, 3, 4,
8, 5,
0, 2,
0, 1, 4,
1, 4, 1,
3, 1,
3, 1,
3, 1, 3,
1, 4, 1,
3
};
static const short yydefact[] =
{ 3,
0, 8,
0, 0, 14,
0, 1, 0,
0, 5,
0, 0,
0, 0, 31,
0, 8,
4, 0, 0,
0, 19,
19, 0, 0,
0, 36, 26,
0, 23,
0, 25,
13, 0, 6,
2, 0, 11,
12, 0,
9, 0,
0, 0, 0,
46, 48, 0,
40, 42,
44, 0,
0, 0,
0, 31, 22,
0, 15, 0,
7, 0,
0, 0, 17,
0, 0, 31,
0, 0,
0, 31,
0, 0, 38,
0, 24, 27,
0, 0,
0, 18,
0, 49, 0,
33, 41, 43,
45, 28,
0, 0,
37, 35, 0,
20, 0, 16,
47, 31,
30, 0,
39, 0, 0,
32, 0, 0,
21, 31,
0, 29,
0, 10, 0,
0, 0
};
static const short yydefgoto[] =
{ 115,
2, 4,
11, 5, 40,
41, 9, 16,
17, 43,
63, 28,
29, 30, 101,
31, 32, 74,
75, 49,
50, 51
};
static const short yypact[] =
{ 18,
-22,-32768, 40,
51, 46, 32,-32768, 32,
23,-32768,
14, 42,
33, 34, -14,
56,-32768,-32768, 37, 60,
35, 59,
59, -5, -5,
39, 24,-32768, 1,-32768,
67,-32768,-32768, -3,-32768,-32768, 61,-32768,-32768, 66,
-32768, 32, 70,
72, -5, 69,-32768,
55, 20, 73,
-32768, 48, 77,
-5, -5, -14,-32768, -5,-32768, 52,
-32768, 50, 5,
21,-32768, 74, -5,
-14, -5, -5,
-5, -14,
-5, 30,-32768, 75,-32768,-32768, 78,
35,
32,-32768, 81,-32768, 31,
57, 86, 73,-32768,-32768,
62, -5,-32768,-32768, 82,-32768, 53,-32768,-32768, -14,
-32768, -5,-32768, 63,
35,-32768, 65, 83,-32768,
-14,
80,-32768, 21,-32768, 92,
95,-32768
};
static const short yypgoto[] =
{-32768,
-32768,-32768, -6, 84,
-75,
-60,-32768,-32768,-32768, 76,
-32768, -2,-32768, -53,-32768,-32768,-32768, 36,
-24, 38,
41, 29
};
#define YYLAST 111
static const short yytable[] = { 48,
52, 12,
77, 83, 96,
45, 18, 56,
15, 3,
24, 81,
8, 25, 86,
26, 82, 27,
90, 15,
66, 19,
69, 70, 57,
20, 46, 47,
-34, 109,
76, 59,
1, 78, 54, 62,
55, 92, 92,
38,
39, 93,
99, 13, 14,
15, 106, 21,
91, 19,
6, 37,
114, 38, 39,
80, 112, 19,
105, 7,
19, 8,
33, 10, 22,
23, 36, 103,
35, 42,
53, 58,
61, 60, 97,
64, 72, 107,
65, 67,
68, 73,
71, 100, 79,
84, 95, 98,
94, 70,
104, 116,
102, 110, 117,
108, 111, 113,
44, 89,
34, 0,
85, 0, 0,
0, 87, 0,
0, 0,
88
};
static const short yycheck[] =
{ 24,
25, 8,
56, 64, 80,
11, 9, 7,
23, 32,
25, 7,
16, 28, 68,
30, 12, 32,
72, 23,
45, 8,
3, 4, 24,
12, 32, 33,
5, 105,
55, 34,
15, 58, 11,
42, 13, 8,
8, 19,
20, 12,
12, 21, 22,
23, 100, 6,
73, 8,
11, 17,
113, 19, 20,
6, 110, 8,
6, 9,
8, 16, 7,
32, 32, 32,
7, 92, 32,
11,
32, 5,
7, 13, 81,
6, 29, 102,
7, 11,
26, 5,
10, 27, 33,
12, 9, 7,
14, 4,
9, 0,
31, 29, 0,
33, 14, 18, 23,
71,
17, -1,
67, -1, -1,
-1, 69, -1,
-1, -1,
70
};
/* -*-C-*- Note
some compilers choke on comments on `#line' lines. */
/* Skeleton output parser for bison,
Copyright (C) 1984, 1989, 1990
Free Software Foundation, Inc.
This program is free software;
you can redistribute it and/or modify
it
under the terms of the GNU General Public License as published by
the
Free Software Foundation; either version 2, or (at your option)
any
later version.
This program is distributed in
the hope that it will be useful,
but
WITHOUT ANY WARRANTY; without even the implied warranty of
MERCHANTABILITY
or FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE.
See the
GNU General
Public License for more details.
You should have received a copy
of the GNU General Public License
along
with this program; if not, write to the Free Software
Foundation, Inc., 675 Mass Ave, Cambridge, MA 02139, USA. */
/* As a special exception, when this file is
copied by Bison into a
Bison output file, you may use
that output file without restriction.
This special exception was
added by the Free Software Foundation
in
version 1.24 of Bison. */
#ifndef alloca
#ifdef __GNUC__
#define alloca __builtin_alloca
#else /* not GNU C. */
#if (!defined (__STDC__) && defined (sparc)) || defined (__sparc__) ||
defined (__sparc) || defined (__sgi)
#include <alloca.h>
#else /* not sparc */
#if defined (MSDOS) && !defined
(__TURBOC__)
#include <malloc.h>
#else /* not MSDOS, or __TURBOC__ */
#if defined(_AIX)
#include <malloc.h>
#pragma
alloca
#else /* not MSDOS, __TURBOC__, or _AIX */
#ifdef __hpux
#ifdef __cplusplus
extern "C" {
void *alloca (unsigned int);
};
#else /* not __cplusplus */
void *alloca ();
#endif /* not __cplusplus
*/
#endif /* __hpux */
#endif /* not _AIX */
#endif /* not MSDOS, or __TURBOC__ */
#endif /* not sparc. */
#endif /* not GNU C. */
#endif /* alloca not
defined. */
/* This is the parser code that is written into
each bison parser
when
the %semantic_parser declaration is not specified in
the grammar.
It was written by Richard
Stallman by simplifying the hairy parser
used
when %semantic_parser is specified. */
/* Note: there must be only one dollar sign in this file.
It is replaced by the list of
actions, each action
as one
case of the switch. */
#define yyerrok (yyerrstatus = 0)
#define yyclearin (yychar = YYEMPTY)
#define YYEMPTY -2
#define YYEOF 0
#define YYACCEPT return(0)
#define YYABORT return(1)
#define YYERROR goto yyerrlab1
/* Like YYERROR except do call yyerror.
This remains here temporarily
to ease the
transition
to the new meaning of YYERROR, for GCC.
Once GCC version 2 has
supplanted version 1, this can go. */
#define YYFAIL goto yyerrlab
#define YYRECOVERING() (!!yyerrstatus)
#define YYBACKUP(token, value) \
do \
if (yychar == YYEMPTY && yylen
== 1) \
{ yychar = (token), yylval =
(value); \
yychar1 = YYTRANSLATE (yychar); \
YYPOPSTACK; \
goto yybackup; \
} \
else \
{ yyerror ("syntax error: cannot back up");
YYERROR; } \
while (0)
#define YYTERROR 1
#define YYERRCODE 256
#ifndef YYPURE
#define YYLEX yylex()
#endif
#ifdef YYPURE
#ifdef YYLSP_NEEDED
#ifdef YYLEX_PARAM
#define YYLEX yylex(&yylval, &yylloc, YYLEX_PARAM)
#else
#define YYLEX yylex(&yylval, &yylloc)
#endif
#else /* not YYLSP_NEEDED */
#ifdef YYLEX_PARAM
#define YYLEX yylex(&yylval, YYLEX_PARAM)
#else
#define YYLEX yylex(&yylval)
#endif
#endif /* not YYLSP_NEEDED */
#endif
/* If nonreentrant, generate the variables
here */
#ifndef YYPURE
int yychar; /* the lookahead
symbol */
YYSTYPE yylval; /* the semantic value of the */
/* lookahead
symbol */
#ifdef YYLSP_NEEDED
YYLTYPE yylloc; /*
location data for the lookahead */
/* symbol */
#endif
int yynerrs; /* number of parse errors so far */
#endif /* not YYPURE */
#if YYDEBUG != 0
int yydebug; /* nonzero means print parse trace */
/* Since this is uninitialized,
it does not stop multiple parsers
from
coexisting. */
#endif
/* YYINITDEPTH
indicates the initial size of the parser's stacks */
#ifndef YYINITDEPTH
#define YYINITDEPTH 200
#endif
/* YYMAXDEPTH
is the maximum size the stacks can grow to
(effective only if the built-in stack extension method is used). */
#if YYMAXDEPTH == 0
#undef YYMAXDEPTH
#endif
#ifndef YYMAXDEPTH
#define YYMAXDEPTH 10000
#endif
/* Prevent warning if -Wstrict-prototypes. */
#ifdef __GNUC__
int yyparse
(void);
#endif
#if __GNUC__ > 1 /* GNU C
and GNU C++ define this. */
#define __yy_memcpy(TO,FROM,COUNT) __builtin_memcpy(TO,FROM,COUNT)
#else /* not GNU
C or C++ */
#ifndef __cplusplus
/* This is the most reliable way to avoid
incompatibilities
in
available built-in functions on various systems. */
static void
__yy_memcpy (to, from, count)
char
*to;
char
*from;
int count;
{
register
char *f = from;
register
char *t = to;
register
int i = count;
while (i-- > 0)
*t++ = *f++;
}
#else /* __cplusplus */
/* This is the most reliable way to avoid
incompatibilities
in
available built-in functions on various systems. */
static void
__yy_memcpy (char *to, char *from, int count)
{
register
char *f = from;
register
char *t = to;
register
int i = count;
while (i-- > 0)
*t++ = *f++;
}
#endif
#endif
/* The user can define YYPARSE_PARAM as the
name of an argument to be passed
into yyparse. The
argument should have type void *.
It should actually point to an
object.
Grammar actions can access the
variable by casting it
to the
proper pointer type. */
#ifdef YYPARSE_PARAM
#ifdef __cplusplus
#define YYPARSE_PARAM_ARG void *YYPARSE_PARAM
#define YYPARSE_PARAM_DECL
#else /* not __cplusplus */
#define YYPARSE_PARAM_ARG YYPARSE_PARAM
#define YYPARSE_PARAM_DECL void *YYPARSE_PARAM;
#endif /* not __cplusplus
*/
#else /* not YYPARSE_PARAM */
#define YYPARSE_PARAM_ARG
#define YYPARSE_PARAM_DECL
#endif /* not YYPARSE_PARAM */
int
yyparse(YYPARSE_PARAM_ARG)
YYPARSE_PARAM_DECL
{
register
int yystate;
register
int yyn;
register
short *yyssp;
register
YYSTYPE *yyvsp;
int yyerrstatus; /*
number of tokens to shift before error messages enabled */
int yychar1 = 0; /* lookahead token as
an internal (translated) token number */
short yyssa[YYINITDEPTH]; /*
the state stack */
YYSTYPE yyvsa[YYINITDEPTH]; /* the
semantic value stack */
short *yyss = yyssa; /*
refer to the stacks thru separate pointers */
YYSTYPE *yyvs
= yyvsa; /* to allow yyoverflow to reallocate them elsewhere */
#ifdef YYLSP_NEEDED
YYLTYPE yylsa[YYINITDEPTH]; /* the
location stack */
YYLTYPE *yyls
= yylsa;
YYLTYPE *yylsp;
#define YYPOPSTACK (yyvsp--, yyssp--, yylsp--)
#else
#define YYPOPSTACK (yyvsp--, yyssp--)
#endif
int yystacksize =
YYINITDEPTH;
#ifdef YYPURE
int yychar;
YYSTYPE yylval;
int yynerrs;
#ifdef YYLSP_NEEDED
YYLTYPE yylloc;
#endif
#endif
YYSTYPE yyval; /* the variable used to return */
/* semantic values
from the action */
/* routines */
int yylen;
#if YYDEBUG != 0
if (yydebug)
fprintf(stderr,
"Starting parse\n");
#endif
yystate = 0;
yyerrstatus = 0;
yynerrs = 0;
yychar = YYEMPTY; /*
Cause a token to be read. */
/* Initialize stack pointers.
Waste one element of value
and location stack
so that
they stay on the same level as the state stack.
The wasted elements are never
initialized. */
yyssp = yyss - 1;
yyvsp = yyvs;
#ifdef YYLSP_NEEDED
yylsp = yyls;
#endif
/* Push a new state, which is found in yystate . */
/* In all cases, when you get here, the value
and location stacks
have
just been pushed. so pushing a state here evens the
stacks. */
yynewstate:
*++yyssp
= yystate;
if (yyssp >= yyss + yystacksize - 1)
{
/* Give user a chance to
reallocate the stack */
/* Use copies of these so
that the &'s don't force the real ones into
memory. */
YYSTYPE *yyvs1 = yyvs;
short
*yyss1 = yyss;
#ifdef YYLSP_NEEDED
YYLTYPE *yyls1 = yyls;
#endif
/* Get the current used size
of the three stacks, in elements. */
int size = yyssp - yyss + 1;
#ifdef yyoverflow
/* Each
stack pointer address is followed by the size of
the data in use in
that stack, in bytes. */
#ifdef YYLSP_NEEDED
/* This
used to be a conditional around just the two extra args,
but that might be
undefined if yyoverflow is a macro. */
yyoverflow("parser
stack overflow",
&yyss1, size * sizeof
(*yyssp),
&yyvs1, size * sizeof
(*yyvsp),
&yyls1, size * sizeof
(*yylsp),
&yystacksize);
#else
yyoverflow("parser
stack overflow",
&yyss1, size * sizeof
(*yyssp),
&yyvs1, size * sizeof
(*yyvsp),
&yystacksize);
#endif
yyss = yyss1; yyvs = yyvs1;
#ifdef YYLSP_NEEDED
yyls = yyls1;
#endif
#else /* no yyoverflow */
/* Extend
the stack our own way. */
if
(yystacksize >= YYMAXDEPTH)
{
yyerror("parser stack overflow");
return 2;
}
yystacksize *= 2;
if
(yystacksize > YYMAXDEPTH)
yystacksize = YYMAXDEPTH;
yyss = (short *) alloca (yystacksize * sizeof (*yyssp));
__yy_memcpy
((char *)yyss, (char
*)yyss1, size * sizeof (*yyssp));
yyvs = (YYSTYPE *) alloca (yystacksize * sizeof (*yyvsp));
__yy_memcpy
((char *)yyvs, (char
*)yyvs1, size * sizeof (*yyvsp));
#ifdef YYLSP_NEEDED
yyls = (YYLTYPE *) alloca (yystacksize * sizeof (*yylsp));
__yy_memcpy
((char *)yyls, (char
*)yyls1, size * sizeof (*yylsp));
#endif
#endif /* no yyoverflow
*/
yyssp = yyss + size - 1;
yyvsp = yyvs + size - 1;
#ifdef YYLSP_NEEDED
yylsp = yyls + size - 1;
#endif
#if YYDEBUG != 0
if
(yydebug)
fprintf(stderr,
"Stack size increased to %d\n", yystacksize);
#endif
if
(yyssp >= yyss + yystacksize - 1)
YYABORT;
}
#if YYDEBUG != 0
if (yydebug)
fprintf(stderr,
"Entering state %d\n", yystate);
#endif
goto yybackup;
yybackup:
/* Do appropriate processing given the current state. */
/* Read a lookahead token if we need one and
don't already have one. */
/* yyresume: */
/* First try to decide what to
do without reference to lookahead token. */
yyn = yypact[yystate];
if (yyn == YYFLAG)
goto yydefault;
/* Not known => get a lookahead token if don't already have one. */
/* yychar
is either YYEMPTY or YYEOF
or a
valid token in external form. */
if (yychar == YYEMPTY)
{
#if YYDEBUG != 0
if
(yydebug)
fprintf(stderr,
"Reading a token: ");
#endif
yychar = YYLEX;
}
/* Convert token to internal
form (in yychar1) for indexing tables with */
if (yychar <= 0) /*
This means end of input. */
{
yychar1 = 0;
yychar = YYEOF; /*
Don't call YYLEX any more */
#if YYDEBUG != 0
if
(yydebug)
fprintf(stderr,
"Now at end of input.\n");
#endif
}
else
{
yychar1 = YYTRANSLATE(yychar);
#if YYDEBUG != 0
if (yydebug)
{
fprintf
(stderr, "Next token is %d (%s", yychar, yytname[yychar1]);
/* Give the individual parser a way to print
the precise meaning
of a token, for
further debugging info. */
#ifdef YYPRINT
YYPRINT (stderr, yychar, yylval);
#endif
fprintf
(stderr, ")\n");
}
#endif
}
yyn += yychar1;
if (yyn < 0 || yyn > YYLAST || yycheck[yyn] != yychar1)
goto yydefault;
yyn = yytable[yyn];
/* yyn
is what to do for this token type in this state.
Negative => reduce, -yyn is rule number.
Positive => shift, yyn is new state.
New state is final state
=> don't bother to shift,
just
return success.
0,
or most negative number => error. */
if (yyn < 0)
{
if
(yyn == YYFLAG)
goto yyerrlab;
yyn = -yyn;
goto yyreduce;
}
else if
(yyn == 0)
goto yyerrlab;
if (yyn == YYFINAL)
YYACCEPT;
/* Shift the lookahead
token. */
#if YYDEBUG != 0
if (yydebug)
fprintf(stderr,
"Shifting token %d (%s), ", yychar, yytname[yychar1]);
#endif
/* Discard the token being
shifted unless it is eof. */
if (yychar != YYEOF)
yychar = YYEMPTY;
*++yyvsp
= yylval;
#ifdef YYLSP_NEEDED
*++yylsp
= yylloc;
#endif
/* count tokens shifted since
error; after three, turn off error status.
*/
if (yyerrstatus) yyerrstatus--;
yystate = yyn;
goto yynewstate;
/* Do the default action for the current state. */
yydefault:
yyn = yydefact[yystate];
if (yyn == 0)
goto yyerrlab;
/* Do a reduction. yyn is the number of a rule to
reduce with. */
yyreduce:
yylen = yyr2[yyn];
if (yylen > 0)
yyval = yyvsp[1-yylen]; /*
implement default value of the action */
#if YYDEBUG != 0
if (yydebug)
{
int i;
fprintf (stderr,
"Reducing via rule %d (line %d), ",
yyn,
yyrline[yyn]);
/* Print the symbols being
reduced, and their result. */
for
(i = yyprhs[yyn]; yyrhs[i]
> 0; i++)
fprintf (stderr, "%s
", yytname[yyrhs[i]]);
fprintf (stderr, "
-> %s\n", yytnaame[yyr1[yyn]]);
}
#endif
switch
(yyn) {
}
/* the action file gets copied
in in place of this dollarsign
*/
yyvsp -= yylen;
yyssp -= yylen;
#ifdef YYLSP_NEEDED
yylsp -= yylen;
#endif
#if YYDEBUG != 0
if (yydebug)
{
short
*ssp1 = yyss - 1;
fprintf (stderr,
"state stack now");
while
(ssp1 != yyssp)
fprintf (stderr, "
%d", *++ssp1);
fprintf (stderr,
"\n");
}
#endif
*++yyvsp
= yyval;
#ifdef YYLSP_NEEDED
yylsp++;
if (yylen == 0)
{
yylsp->first_line = yylloc.first_line;
yylsp->first_column = yylloc.first_column;
yylsp->last_line =
(yylsp-1)->last_line;
yylsp->last_column =
(yylsp-1)->last_column;
yylsp->text = 0;
}
else
{
yylsp->last_line =
(yylsp+yylen-1)->last_line;
yylsp->last_column =
(yylsp+yylen-1)->last_column;
}
#endif
/* Now "shift" the
result of the reduction.
Determine what state that
goes to,
based
on the state we popped back to
and
the rule number reduced by. */
yyn = yyr1[yyn];
yystate = yypgoto[yyn - YYNTBASE] + *yyssp;
if (yystate >= 0 && yystate
<= YYLAST && yycheck[yystate]
== *yyssp)
yystate = yytable[yystate];
else
yystate = yydefgoto[yyn - YYNTBASE];
goto yynewstate;
yyerrlab: /* here on detecting error */
if (! yyerrstatus)
/* If not already recovering
from an error, report this error. */
{
++yynerrs;
#ifdef YYERROR_VERBOSE
yyn = yypact[yystate];
if
(yyn > YYFLAG && yyn
< YYLAST)
{
int
size = 0;
char *msg;
int
x, count;
count = 0;
/* Start X at -yyn
if nec to avoid negative
indexes in yycheck.
*/
for (x = (yyn < 0 ? -yyn : 0);
x < (sizeof(yytname)
/ sizeof(char *)); x++)
if (yycheck[x + yyn] == x)
size += strlen(yytname[x]) + 15, count++;
msg
= (char *) malloc(size + 15);
if (msg != 0)
{
strcpy(msg, "parse error");
if (count <
5)
{
count = 0;
for (x = (yyn < 0 ? -yyn : 0);
x < (sizeof(yytname)
/ sizeof(char *)); x++)
if (yycheck[x + yyn] == x)
{
strcat(msg, count == 0 ? ", expecting `"
: " or `");
strcat(msg, yytname[x]);
strcat(msg, "'");
count++;
}
}
yyerror(msg);
free(msg);
}
else
yyerror
("parse error; also virtual memory exceeded");
}
else
#endif /* YYERROR_VERBOSE
*/
yyerror("parse
error");
}
goto yyerrlab1;
yyerrlab1: /* here on error
raised explicitly by an action */
if (yyerrstatus == 3)
{
/* if just tried and failed
to reuse lookahead token after an error, discard
it. */
/* return failure if at end
of input */
if
(yychar == YYEOF)
YYABORT;
#if YYDEBUG != 0
if
(yydebug)
fprintf(stderr,
"Discarding token %d (%s).\n", yychar, yytname[yychar1]);
#endif
yychar = YYEMPTY;
}
/* Else
will try to reuse lookahead token
after
shifting the error token. */
yyerrstatus = 3; /*
Each real token shifted decrements this */
goto yyerrhandle;
yyerrdefault: /* current state does not do anything special
for the error token. */
#if 0
/* This
is wrong; only states that explicitly want error tokens
should
shift them. */
yyn = yydefact[yystate]; /* If its
default is to accept any token, ok.
Otherwise pop it.*/
if (yyn) goto yydefault;
#endif
yyerrpop: /* pop the current state because it cannot
handle the error token */
if (yyssp == yyss) YYABORT;
yyvsp--;
yystate = *--yyssp;
#ifdef YYLSP_NEEDED
yylsp--;
#endif
#if YYDEBUG != 0
if (yydebug)
{
short
*ssp1 = yyss - 1;
fprintf (stderr,
"Error: state stack now");
while
(ssp1 != yyssp)
fprintf (stderr, "
%d", *++ssp1);
fprintf (stderr,
"\n");
}
#endif
yyerrhandle:
yyn = yypact[yystate];
if (yyn == YYFLAG)
goto yyerrdefault;
yyn += YYTERROR;
if (yyn < 0 || yyn > YYLAST || yycheck[yyn] != YYTERROR)
goto yyerrdefault;
yyn = yytable[yyn];
if (yyn < 0)
{
if
(yyn == YYFLAG)
goto yyerrpop;
yyn = -yyn;
goto yyreduce;
}
else if
(yyn == 0)
goto yyerrpop;
if (yyn == YYFINAL)
YYACCEPT;
#if YYDEBUG != 0
if (yydebug)
fprintf(stderr,
"Shifting error token, ");
#endif
*++yyvsp
= yylval;
#ifdef YYLSP_NEEDED
*++yylsp
= yylloc;
#endif
yystate = yyn;
goto yynewstate;
}
#line 120 "pas(2).y"
int error (char * s){ /* Called by yyparse
on error */
fprintf(stderr, "%s: Error, ver linea: %d", yyTexto(), ln);
if(msg != NULL && *msg != '\0')
printf(":
%s", msg);
printf("\n");
// printf(stderr,
"%s: Error, ver linea: %d", yyTexto());
return 0;
}
main ()
{
printf("_______________________________________________________________________\n");
printf("Digite el programa a analizar, para terminar escriba \"eof\"\n");
printf("_______________________________________________________________________\n\n");
yyparse ();
}

![Cuadro de texto: %{
#include "pas(2).tab.h"
int ln = 1;
char * yyTexto() {
return yytext;
}
%}
%option noyywrap
delim [ \t]
blancos {delim}+
letra [A-Za-z]
digito [0-9]
id {letra}({letra}|{digito})*
numero {digito}+(\.{digito}+)?
coment {[^}\n]}
%%
{blancos} {/*no realiza accion*/}
"\n" {ln++;}
"=" {return (OPREL);}
"<>" {return (OPREL);}
"<" {return (OPREL);}
"<=" {return (OPREL);}
">=" {return (OPREL);}
">" {return (OPREL);}
"+" {return (OPSuma);}
"-" {return (OPSuma);}
":=" {return (OPAsigna);}
":" {return (DOSP);}
";" {return (PTOCOMA);}
"." {return (PTO);}
"," {return (COMA);}
"*" {return (OPMult);}
"/" {return (OPMult);}
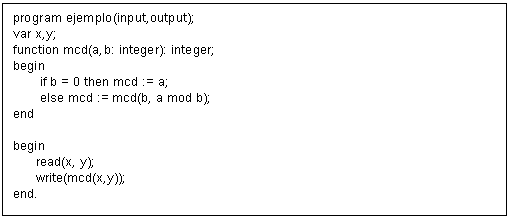
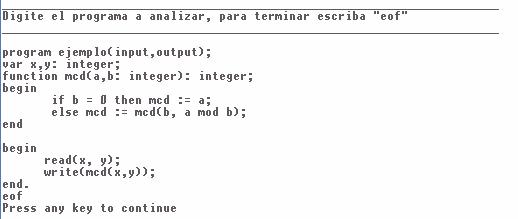
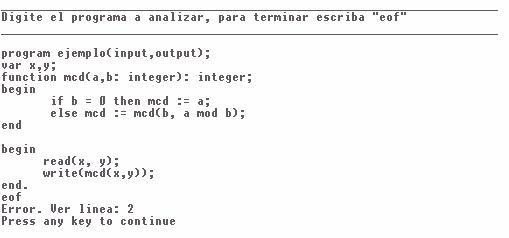
div {return (OPMult);}](t8solA11727_archivos/image002.gif) Para este caso el archivo de entrada para Flex fue:
Para este caso el archivo de entrada para Flex fue:![Cuadro de texto: mod {return (OPMult);}
and {return (OPMult);}
"(" { return(PABRE); }
")" { return(PCIERRA); }
"[" { return(PABREC); }
"]" { return(PCIERRAC); }
"{" { return(LLAVEA); }
"}" { return(LLAVEC); }
program {return (PROG);}
var {return (VAR);}
array {return (ARR);}
of {return (OF);}
integer {return (INT);}
real {return (REAL);}
function {return (FUNC);}
procedure {return (PROC);}
begin {return (BEG);}
end {return (END);}
if {return (IF);}
then {return (THEN);}
else {return (ELSE);}
while {return (WHILE);}
do {return (DO);}
for {return (FOR);}
to {return (TO);}
{id} {return (ID);}
{numero} {return (NUM);}
%%](t8solA11727_archivos/image003.gif)